Background on Data Governance
What it used to be
The term Data Governance used to refer to data cataloging or regulatory compliance procedures
What it is now
Data Governance now is a strategic approach to manage information assets companywide
Then
-
Data Cataloging at the business unit level
-
Regulatory Compliance at the IT level
-
Siloed approach
Now
-
Strategic Planning of Information Assets
-
Rules, Standards, and Procedures
-
Companywide approach
Definition of Data Governance
Data Governance refers to the strategic planning of the organization’s management of its information assets culminating in implementation of the right business processes, policies, and standards using the appropriate technology to achieve the organization’s mission and, in the process, improves its competitive advantage.
Getting Started with Data Governance at Your Organization
The following steps can help you launch a Data Governace initiative at your organizations and help sell it to key stakeholders:
- Determine Value and Mission of the Data Governance Program
- Identify High Value Use Cases
- Stakeholder Identification and Engagement
- Develop framework and Plan
Develop a values statement based on the organization’s mission and vision. This statement should state why Data Governance is beneficial to this organization how it will introduce value.
Demonstrate value in Data governance by identifying easy to implement/high reward policies or procedures.
Identify the appropriate stakeholders from management and business operations. An initial meeting is crucial to present the value of the initiative and agree on the vision.
Develop the framework of how Data Governance will be implemented and enforced throughout the organization.
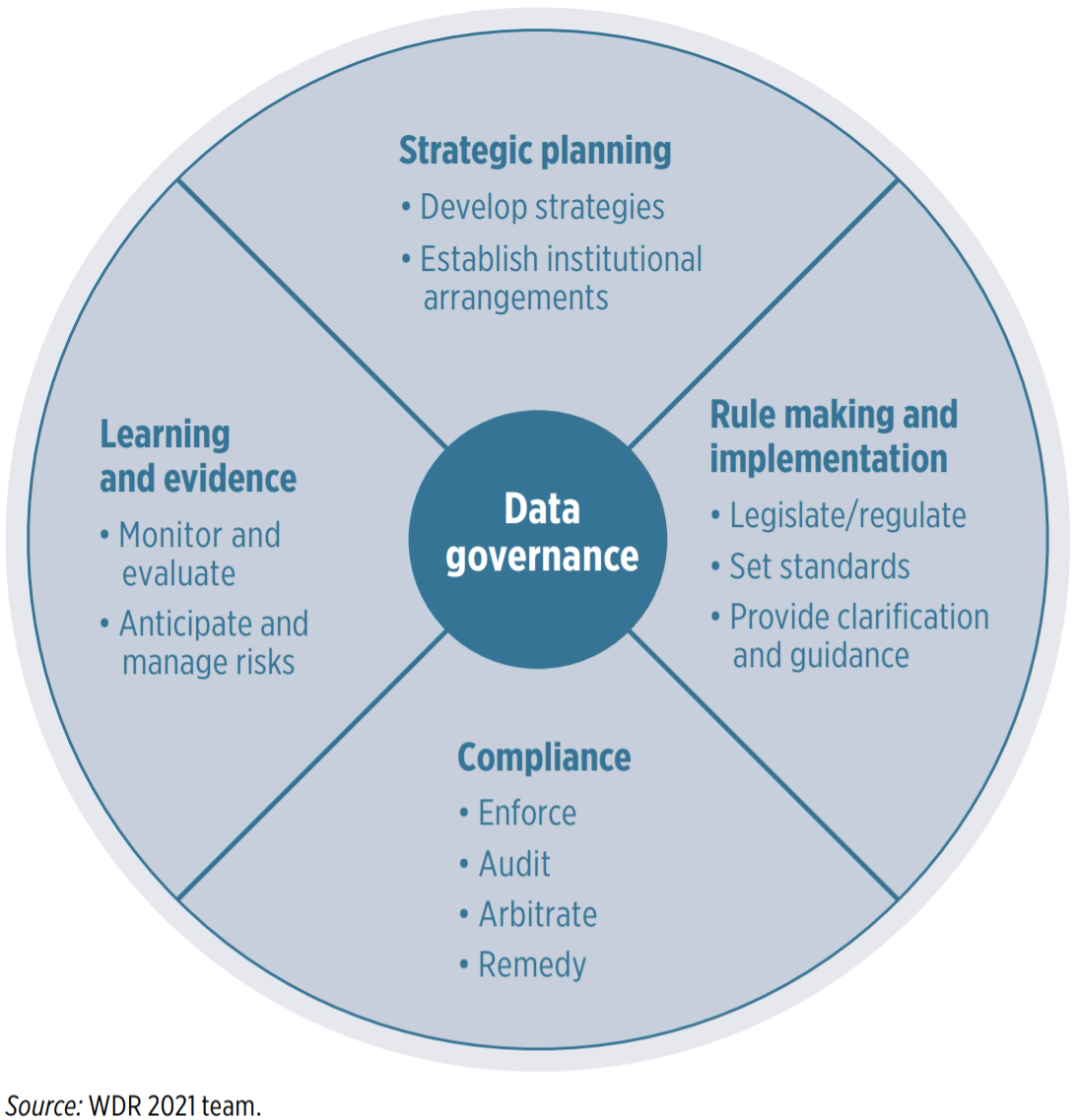
Principles of Data Governance
A succesful Data Governance program should have its roots based on a set of principles that are relevant and bring value to the organization. The following principles are a set of essential activities a successful DG program should introduce.
- Transparency
- Auditability
- Quality
- Consistency
- Ownership
- Change Management
Data Governance should create clear roles, procedures, decision and controls pertaining to data.
Data Governance should promote documentation for all data related activities for compliance and audit matters.
Data Governance should improve quality, accuracy, and ease of access to data.
Data Governance should standardize data formats, technologies, and procedures across the organization.
Data Governance should define clear data owners, stewards, or contributors.
Data Governance should manage all data related changes and promote continuous improvement.
Data Governance Program Deliverables
Each DG program must produce a version of the following deliverables. While each organization's needs are uniqure the following components provide a generic and universal minimum requirement that a mature and holistic DG program must provide.
- Mission and Vision
-
Proactively define/align rules
-
Provide ongoing, boundary-spanning protection and services to data stakeholders
-
React to and resolve issues arising from non-compliance with rules
- Data Governance Office
-
The DGO runs and enforces the program across the organization
-
Keeps track of Data Stakeholders and Stewards
-
Provides liaisons to other disciplines and programs, such as Data Quality, Compliance, Privacy, Security, Architecture, and IT Governance
-
Collects and aligns policies, standards, and guidelines from these stakeholder groups
-
Arranges for the providing of information and analysis to IT projects as requested
-
Facilitates and coordinates data analysis and issue analysis projects
-
Facilitates and coordinates meetings of Data Stewards
-
Collects metrics and success measures and reports on them to data stakeholders
- Data Stewardship
-
Assign subject matter experts as points of contact for the data and parts of the program they oversee
-
Data Stewards manage their data and systems in accordance with the established policies and procedures outlines by the DGO
- Data Standards
-
Standard formats of data should be unified across the organization
-
Technologies should also be standardized whenever feasible
- Data Policies
-
The policies guide and control the rules regarding all aspects of data quality, security, and use throughout its lifecycle
- DG Assessment Plan (KPI’s and successs metrics)
-
Quantitative metrics should be employed to measure business value of DG policies
-
DG dashboard that includes key metrics such as data value or DG program cost is a good way to monitor progress
- Decision Rights
-
DG should dictate who gets to make the decision, when, and using what process
-
DG should establish where the decision rights are before making any data related decision
Maturity Models
Maturity Models are a tool to assess where the organization is in the progress of implementing a change. They generally produce a scorecard that measures several factors in the program. The most useful two maturity models when it comes to Data Governance are IBM’s and Gartner’s Enterprise Information Management models.